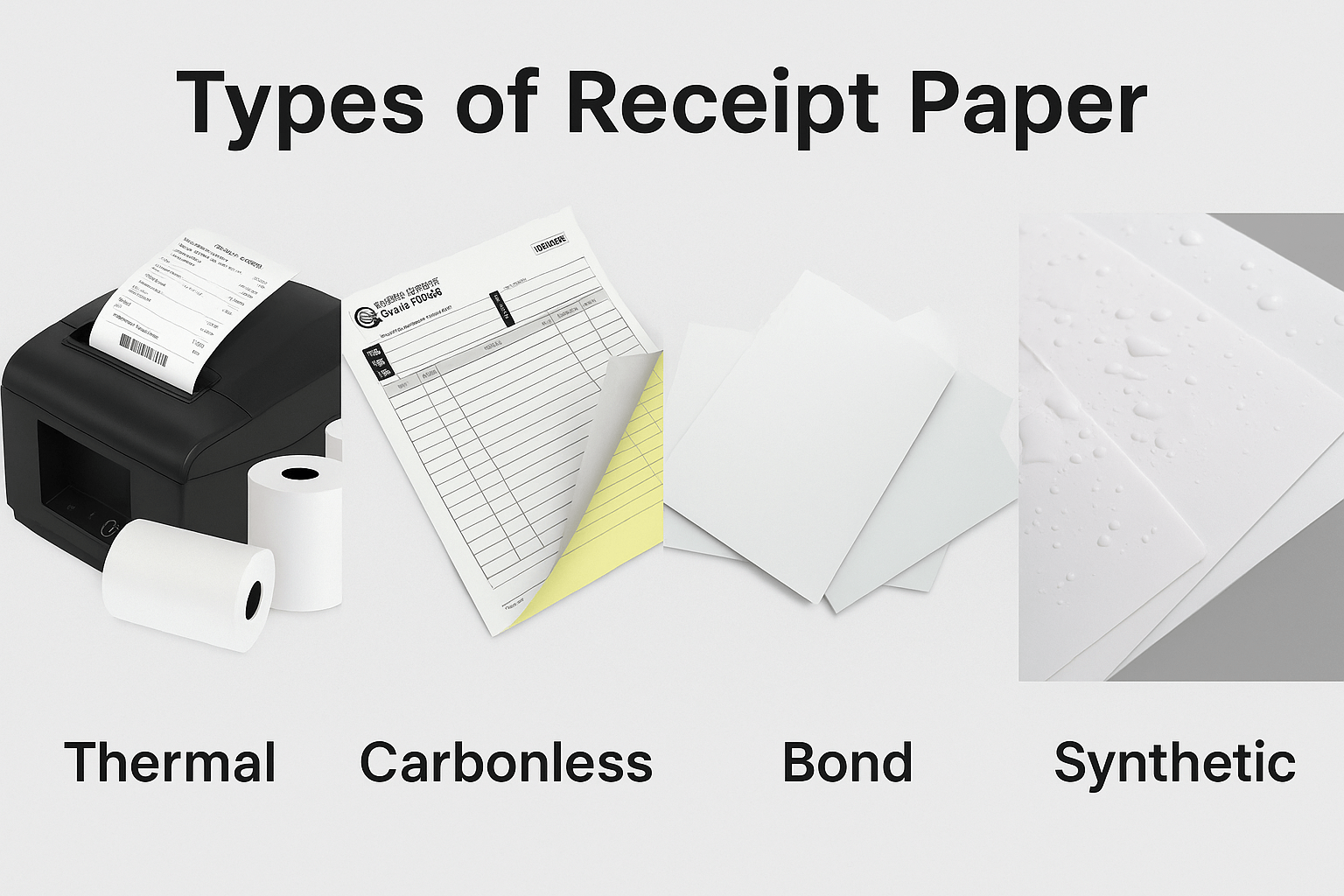
Choosing the right receipt paper type can impact more than you think. Ever had a receipt that faded in days? That’s not just bad luck—it’s about using the wrong paper. Different businesses need different types to print clearly and last longer.
In this post, you’ll explore the most common types of receipt paper. We’ll explain how they work, where they’re used, and what makes each one unique. Whether you run a café, shop, or delivery service, this guide will help you pick the best option.
What Is Receipt Paper?
What Does Receipt Paper Do?
Receipt paper is a special kind of paper used to print transaction details. You see it at checkout counters, in restaurants, or when signing for deliveries. It helps businesses give proof of payment, track sales, and manage records. Unlike notebook or printer paper, it’s designed to work fast and efficiently in different types of receipt printers.
How Is It Different from Regular Paper?
At first glance, it may look the same. But receipt paper is built for specific printers and tasks. It often has coatings or chemical layers that react to heat or pressure. Regular paper doesn't. Plus, regular printing paper needs ink, while many receipt papers don't. That’s why receipts feel smoother and look different.
Key Differences at a Glance:
Coating: Receipt paper may have heat-sensitive or chemical coatings; regular paper usually has none.
Ink Use: Receipt paper often prints without ink; regular paper needs ink or toner.
Durability: Some receipt types fade quickly, while plain paper lasts longer but prints slower.
Printer Compatibility: Designed for thermal or impact printers—not for home inkjets.
How Do Receipt Printers Work?
Receipt printers are built for speed and convenience. They usually fall into two types: thermal and impact. Thermal printers use heat to create images on special paper. No ink needed. Impact printers strike the paper through a ribbon—like an old typewriter. Each has a different use.
Main Types of Receipt Printers:
Thermal Printers: Heat reacts with coated paper to print text or images.
Impact Printers: Tiny pins hit a ribbon to transfer ink onto paper.
Liner-free Printers: Specialized thermal printers for sticky or adhesive receipt paper.
Quick Printer Facts:
Thermal printers are faster and quieter.
Impact printers work with plain or carbonless paper.
Some printers support only specific widths and roll sizes.
The Main Types of Receipt Paper
1. Thermal Receipt Paper
Thermal paper reacts to heat instead of ink. It has a chemical coating that darkens when heated by a thermal printer head. You’ll often find it in busy checkout counters because of its speed and simplicity.

How Thermal Printing Works
Heat activates the paper’s special coating to form letters and numbers without ink or ribbons.
The printer head moves quickly over the paper, producing clean, dark images in seconds.
Key Characteristics and Composition
It has a smooth, glossy coating on one side that reacts to heat.
No ink or toner is needed, which makes maintenance cheaper and easier for high-volume use.
Common Use Cases
Used in retail POS systems to quickly generate customer receipts.
Found in ATMs, kiosks, and portable credit card terminals for instant, ink-free printing.
Advantages
Fast and silent output that speeds up customer transactions at checkout counters.
No ink or ribbons needed, which reduces maintenance tasks and ongoing supply costs.
Disadvantages
Text can fade easily if exposed to sunlight, heat, oils, or cleaning chemicals.
Not suitable for storage where printed receipts must remain legible for months or years.
2. Bond Receipt Paper (Also Known as Plain or Woodfree Paper)
Bond paper has no special coatings. It’s made from wood pulp or cotton fiber and relies on ink ribbons or toner. It’s used where print durability and clarity matter more than speed.
What Makes It Different
It doesn’t have a chemical coating and requires ink or ribbons to produce text or images.
The texture is less smooth than thermal paper, and the surface feels more like copy paper.
Suitable Printing Methods
Common Applications
Common in official forms, transaction slips, or reports needing clear and lasting records.
Often found in banking, medical offices, and settings where archives are required.
Advantages
Offers long-lasting prints that are perfect for receipts needing storage or official documentation.
Less sensitive to heat or light, so the printed image remains readable for years.
Disadvantages
Requires ink ribbons, which need replacing and can increase overall printing costs.
Slower and louder operation due to mechanical impact printing technology.
3. Carbonless Copy Paper (NCR Paper)
Carbonless paper creates multiple copies by using pressure and chemicals—no messy carbon sheets required. It’s common in delivery forms, service tickets, and business records.

How It Creates Copies
Pressure applied to the top sheet breaks microcapsules that release dye to the sheet below.
The dye reacts with a clay coating on the lower page, transferring the text or image instantly.
Layered Paper Structure
CB (coated back) is the top layer that receives writing or printer pressure.
CFB (coated front and back) sits in the middle and transfers the image both ways.
CF (coated front) is the bottom layer where the final copy appears.
Where It’s Commonly Used
Used in service industries for invoices, delivery receipts, and signed agreements.
Helpful where businesses keep a copy while giving one to the customer or driver.
Advantages
Creates duplicate or triplicate copies during one single action, reducing paperwork steps.
Cleaner and easier to use than traditional carbon sheets, which smudge and tear.
Disadvantages
4. Synthetic Receipt Paper
Synthetic paper is made from durable plastic-like materials. It’s tough, waterproof, and doesn’t tear easily, making it perfect for environments where paper receipts might get damaged.
What It’s Made Of
Typically crafted from polypropylene or polyester, giving it resistance to moisture and ripping.
It looks like paper but feels slightly stiffer and more durable in your hand.
Ideal Use Cases
Works well in outdoor markets, food trucks, and delivery operations where weather is a factor.
Used in areas where wet or rough conditions could destroy standard paper receipts.
Advantages
Highly resistant to water and damage, even when crumpled or stored in pockets.
Longer-lasting image retention than most thermal options in tough conditions.
Disadvantages
More expensive to purchase, especially compared to standard thermal or bond paper.
Requires printer compatibility, as not all printers can handle its thickness or texture.
5. Linerless Receipt Paper
Linerless paper sticks like a label but prints like a receipt. It doesn’t come with a peel-off backing, making it easier and faster to use in labeling or packaging.
What Makes It Different
Has an adhesive backing but no liner, so there’s no waste or peeling involved.
The paper feeds and prints like standard receipt rolls but can be applied directly to surfaces.
Common Use Examples
Ideal for takeout labels, barcode tags, and packing slips in shipping environments.
Saves time in fast-paced kitchens or warehouses by combining printing and application.
Advantages
No paper liner waste, so rolls last longer and reduce the need for frequent replacements.
Quick and easy to apply, speeding up order prep and labeling for businesses.
Disadvantages
Only works with liner-free printers, which are more specialized and less common.
Not intended for long-term receipts, as the adhesive may degrade over time.
How to Choose the Right Type of Receipt Paper
Consider Your Business Type
Retail Stores with High Customer Flow
For busy retail environments, thermal paper is often preferred due to its fast printing speed and low maintenance. It doesn't require ink or ribbons, making it ideal for high-volume transactions.
Food and Beverage Service Providers
In restaurants and cafes, durability is key. While thermal paper is commonly used, it can be sensitive to heat and light. For a more durable option, consider paper that can withstand spills or frequent handling.
Understand Your Printer Type
Thermal Printers
Thermal printers are efficient and cost-effective, printing quickly without the need for ink. They’re ideal for high-volume printing and are low-maintenance.
Impact Printers
Impact printers use ribbons and are better suited for multi-copy receipts. However, they come with higher operational costs due to the need for ink and ribbons.
Think About Cost vs Long-Term Value
Upfront Paper Costs
Thermal paper may have a higher upfront cost but eliminates the need for ink or ribbons. Non-thermal options like impact paper may be cheaper initially but increase long-term maintenance costs.
Maintenance Costs
While thermal paper reduces maintenance costs by not requiring ink or ribbons, impact paper printers will incur higher ongoing expenses due to the need for consumables.
Evaluate Durability Needs
For customer-facing receipts, thermal paper is typically sufficient. However, for long-term storage or in environments where receipts are exposed to water or heavy handling, opt for more durable options like synthetic paper.
How to Identify Receipt Paper Types
Thermal Paper
Glossy Appearance and Smooth Texture
Thermal paper has a smooth, glossy finish. This is due to a heat-sensitive coating that reacts when exposed to the thermal printhead. The glossy side is where the printing occurs.
Scratch Test: Black Mark Indicates Thermal Side
To identify the thermal side of the paper, try the scratch test. When you scratch the surface, a black mark will appear on the side coated for thermal printing. This is a quick way to confirm the thermal side.
Bond and Carbonless Paper
No Coating on Bond Paper, Dull Surface
Bond paper has no special coating, so it appears matte or dull. It’s typically used for printing multi-copy receipts or forms and has a more textured surface.
Carbonless Paper Has Multiple Layers with Distinct Colors
Carbonless paper is designed for creating copies without the need for carbon sheets. It comes in multiple layers, with each layer featuring different colors. The top layer transfers ink or imprints onto the layer beneath it when pressure is applied.
Tips for Testing Paper Compatibility
Know your printer model and specifications. Different printers may only work with specific paper types like thermal or bond.
Measure the receipt roll’s width and diameter. Make sure the paper fits your printer correctly for proper functionality.
Receipt Paper Sizes and Formats
Common Widths Used in POS Systems
Receipt paper for point-of-sale (POS) systems typically comes in 2-inch, 3-inch, or 4-inch widths. These sizes are the most common for standard receipt printers. The 3-inch width is the most popular for retail transactions, while 2-inch rolls are often used in smaller spaces or for mobile devices.
Importance of Measuring Roll Width and Diameter
When selecting receipt paper, it's essential to measure both the roll width and diameter. The width ensures that the paper will fit into the printer, while the diameter determines how much paper can be loaded at once. If the diameter is too large, it may not fit into your printer's roll holder, causing operational issues.
Matching Paper Size with Printer Slot and Application
The size of the receipt paper should align with both the printer’s capabilities and the intended use. For instance, larger formats may be required for detailed receipts in restaurants or for invoices in certain industries. Smaller formats work better in mobile POS systems or in locations where space is limited. Matching the correct size ensures a seamless fit, preventing paper jams and ensuring compatibility.
Conclusion
Choosing the right receipt paper depends on business needs, printer compatibility, and durability. Thermal paper is ideal for fast printing, while bond paper works well for archival purposes. Carbonless paper provides multiple copies, and synthetic paper is perfect for harsh environments. Always test a small batch before purchasing in bulk.
By understanding your business type and printer model, you can make a well-informed decision. Consider factors like cost, durability, and customization options. Don’t forget to test different paper types before committing to a large order, ensuring the best fit for your specific requirements.
FAQs
1. What’s the best receipt paper for small businesses?
The best receipt paper depends on your business’s needs. Thermal paper is efficient for high-volume printing, while bond paper offers durability at a lower cost.
2. Can I use thermal paper in a regular printer?
No, thermal paper requires a thermal printer to work properly. Regular printers use ink or toner, which won't work on thermal paper.
3. Why do thermal receipts fade, and how can I store them better?
Thermal receipts fade due to heat and light exposure. To preserve them, store receipts in a cool, dark place, away from direct sunlight.
4. How can I tell what kind of receipt paper I’m using?
You can identify thermal paper by its smooth, glossy surface. Bond paper will feel matte, while carbonless paper has multiple layers with distinct colors.
Reference Sources
[1] https://www.sunavin.com/4-common-types-of-receipt-paper/
[2] https://pandapaperroll.com/receipt-paper-types/
[3] https://graphictickets.com/types-of-thermal-paper-and-their-benefits/
[4] https://telemarkcorp.com/everything-you-need-to-know-about-thermal-paper/
[5] https://www.shoeboxed.com/blog/what-are-our-daily-receipt-papers-made-of-3-common-types-of-receipt-paper/
[6] https://www.hprt.com/blog/Receipt-Papers-Explained-Types-BPA-Safety-Concerns-Environmental-Impact.html
[7] https://www.pospaper.com/blogs/news/3-types-of-receipt-paper-what-you-need-to-know
[8] https://www.xprintertech.com/understanding-the-different-paper-types-for-thermal-receipt-printers
[9] https://www.toprollpaper.com/different-types-of-thermal-paper/



























