
Did you know using the wrong paper in your printer could cause costly damage? Many people can't easily tell thermal paper from regular receipts. But knowing the difference can protect your equipment and save money.
In this post, you'll learn simple tests to check if your receipt is thermal paper.
What is Thermal Paper?
Thermal paper is a special type of receipt paper widely used in businesses like supermarkets, restaurants, and banks. Unlike regular paper, it doesn’t need ink or toner to display text or images. Instead, it creates images through a heat-activated chemical reaction.
Composition and Structure
Thermal paper consists of three distinct layers that work together to enable heat-sensitive printing:
| Layer | Description | Function |
| Base Layer | Plain paper foundation | Provides structural support and durability |
| Precoat Layer | Smoothing layer with fillers | Creates an even surface and improves image quality |
| Thermal Layer | Heat-sensitive chemical coating | Changes color when exposed to heat |
The thermal layer contains a mixture of colorless dyes and developers that remain separate until heat is applied. This unique chemical composition is what distinguishes thermal paper from other types of receipt paper.
How Thermal Paper Works
When a thermal printer processes a receipt, it works through a surprisingly simple mechanism:
The thermal printhead applies precise heat to specific areas of the paper
Heat activates the chemical reaction between dyes and developers
The reaction causes the affected areas to change color (typically black)
Text and images appear without any ink or toner being used
This heat-sensitive property makes thermal paper easy to identify - when you scratch the surface with your fingernail, the friction generates enough heat to create a visible mark.
Advantages of Using Thermal Paper
Thermal paper offers several benefits that have made it the preferred choice for receipt printing:
Cost-effective operation - No need for ink, toner, or ribbons
Faster printing speed - Direct thermal printing is quicker than ink-based methods
Crisp, high-definition results - Produces clear text and sharp images
Maintenance simplicity - Fewer moving parts means less printer maintenance
Quiet printing process - Creates less noise than impact printers
4 Proven Methods to Identify Thermal Paper Receipts
It’s easy to confuse thermal paper with other types like bond or carbonless paper. But with a few simple tests, you can confidently identify thermal receipts in seconds.These four reliable methods will help you determine with certainty whether you're dealing with thermal paper or another type of receipt paper.
Method 1: The Fingernail Scratch Test
The fingernail scratch test is the quickest and most convenient way to identify thermal paper. This simple test works because of thermal paper's heat-sensitive properties.

Step-by-step scratch test procedure:
Hold the receipt paper firmly on a flat surface
Use your fingernail to draw a line across the paper with moderate pressure
Observe the paper where you scratched it
Look for a dark mark or line appearing where friction occurred
When you scratch thermal paper, the friction generates heat that activates the chemical coating. This heat causes the dye to change color, typically creating a dark mark. Regular paper will show no reaction to this test.
For complete accuracy, try scratching both sides of the paper. Genuine thermal paper will only show a reaction on the coated side. If neither side shows marks after scratching, you're likely dealing with bond paper or carbonless paper instead.
Method 2: Visual and Tactile Examination
Thermal paper has distinct physical characteristics that can help identify it without any testing.
| Characteristic | Thermal Paper | Bond/Carbonless Paper |
| Surface texture | Very smooth, slightly shiny | Less smooth, more matte finish |
| Thickness | Usually thinner | Typically thicker |
| Feel | Slick, almost waxy | More fibrous |
| Appearance | Uniform, often with slight gloss | More textured |
Method 3: The Heat Test
The heat test leverages thermal paper's core property - its reaction to heat.
To safely perform a heat test:
Hold one end of the paper securely
Briefly hold a lighter flame near (not touching) the back of the paper
Observe any color change on the front side
Remove heat immediately once you see a reaction
When heat is applied, thermal paper will develop a dark mark that gradually fades into the surrounding area. This reaction occurs because the heat activates the chemical coating just as a thermal printer would.
Safety Warning: Use extreme caution with this method. Hold the paper away from flammable materials and only apply heat briefly to avoid fire hazards.
Method 4: Testing with a Thermal Printer
The most definitive test is using an actual thermal printer, as these printers are specifically designed to work with thermal paper.
To conduct this test:
Insert the suspected thermal paper into a thermal printer
Print a test receipt
Observe whether text appears on the paper
A thermal printer will produce clear images on thermal paper without using any ink or ribbon. When non-thermal paper is used in these printers, no printing will appear because there's no chemical coating to react with the heat.
This method is considered the most reliable for identification, especially for business owners who need to ensure they're purchasing the correct paper type for their receipt printers.
Different Types of Receipt Paper Used in Retail
In the retail industry, businesses use three primary types of receipt paper, each with distinct characteristics and purposes.
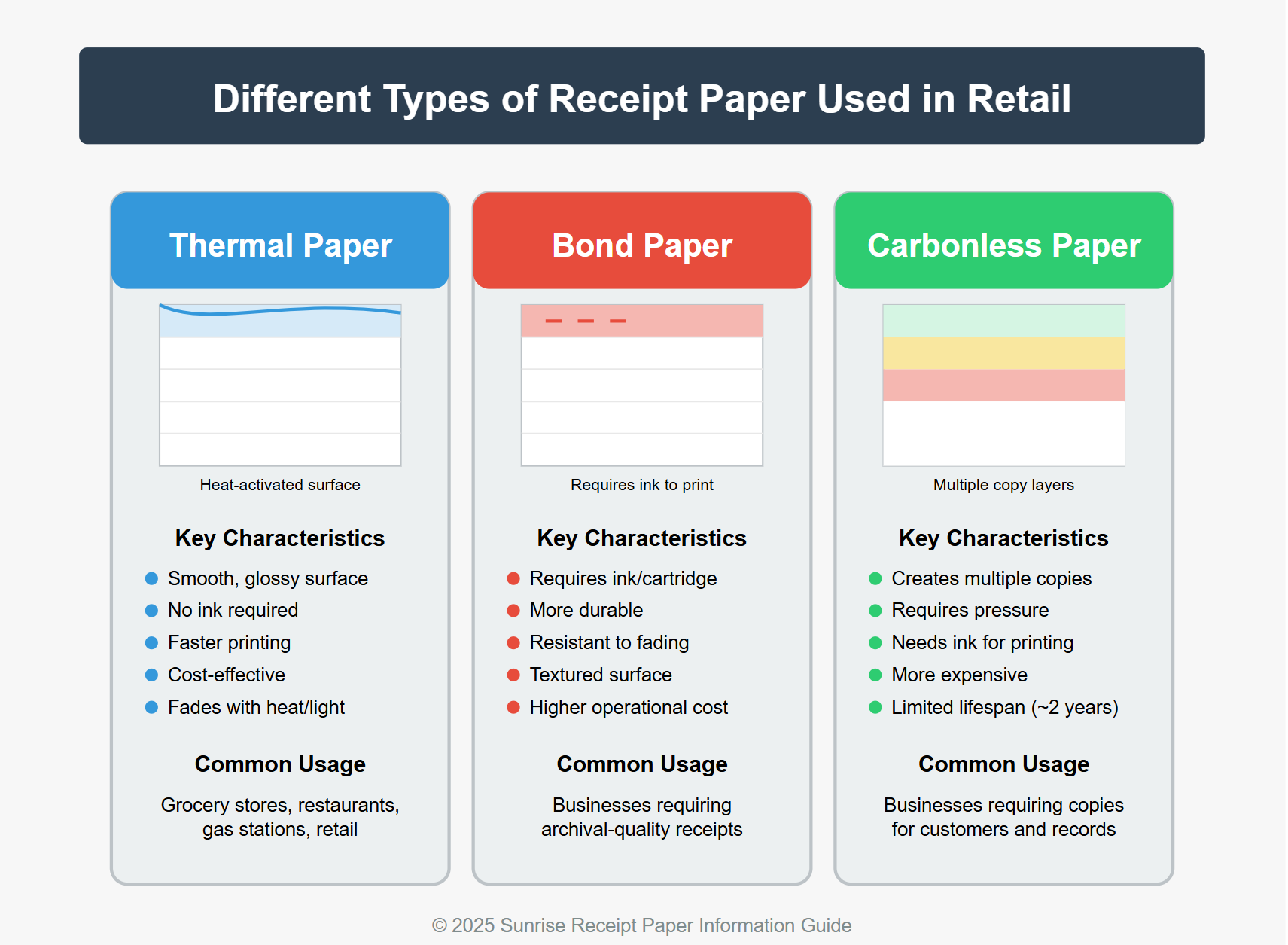
Thermal Paper
Thermal paper stands out as the most widely used receipt paper in modern retail environments. Its defining feature is a chemical coating that changes color when exposed to heat. This technology eliminates the need for ink or toner, making it an economical and efficient choice for high-volume businesses.

Key characteristics of thermal paper:
Smooth, often glossy surface
Reacts to heat by changing color
No ink required for printing
Faster printing speeds
More affordable for daily operations
Susceptible to fading from heat, light, and moisture
Thermal paper is commonly found in grocery stores, restaurants, gas stations, and virtually any business that processes numerous transactions daily.
Bond Paper (Woodfree Paper)
Bond paper, also known as woodfree paper, represents the traditional option for receipt printing. Unlike thermal paper, bond paper doesn't have heat-sensitive properties.
Key characteristics of bond paper:
Requires ink or cartridge to print
More durable than thermal paper
Resistant to fading from heat and light
Less smooth surface compared to thermal paper
Better for long-term document storage
Higher operational costs due to ink requirements
Businesses that need archival-quality receipts often choose bond paper despite its higher operational costs.
Carbonless Paper (NCR Paper)
Carbonless paper (No Carbon Required or NCR paper) creates duplicate copies without carbon sheets. This multi-ply option typically comes in sets of 2-4 sheets in various colors (white, pink, yellow, blue).
Key characteristics of carbonless paper:
Creates multiple copies simultaneously
Requires pressure to transfer content between layers
Needs ink/cartridge for initial printing
Typically more expensive than other options
Limited lifespan (approximately two years)
Environmentally friendlier than carbon paper
This paper type is ideal for businesses requiring receipt copies for both customers and internal records.
Comparison Chart
| Feature | Thermal Paper | Bond Paper | Carbonless Paper |
| Printing method | Heat-activated | Ink required | Ink required + pressure transfer |
| Durability | Low (fades over time) | High | Medium (2-year lifespan) |
| Cost | Low operating cost | Higher due to ink | Highest initial cost |
| Environmental impact | Contains chemicals | Lower chemical content | Biodegradable |
| Multiple copies | No | No | Yes (2-4 plies) |
| Best use case | High-volume retail | Document archiving | Record keeping |
Final Words
You now know four simple ways to identify thermal receipt paper. These include scratch, visual, heat, and printer tests.
Choosing the correct receipt paper protects your printers and saves money. Always test your paper carefully before buying it.
Frequently Asked Questions About Thermal Paper
Q: Can thermal paper be used in regular printers?
A: No, thermal paper cannot be used in regular printers. It requires heat to produce images, while regular printers use ink or toner. Thermal paper only works with thermal printers that apply heat to activate the chemical coating.
Q: How long do thermal paper receipts last?
A: Thermal paper receipts typically last 1-3 years under normal conditions. They fade significantly faster when exposed to heat, direct sunlight, or moisture. Important receipts on thermal paper should be copied or scanned for long-term record keeping.
Q: Are there any health concerns associated with handling thermal paper?
A: Some thermal paper contains BPA or BPS chemicals, which have raised health concerns. These chemicals can be absorbed through skin contact. BPA-free thermal paper options are available and recommended for reducing potential health risks.
Q: Can thermal paper receipts be recycled?
A: Thermal paper receipts are technically recyclable but problematic. The chemical coating can contaminate other recycled paper products. Many recycling facilities recommend disposing of thermal receipts in regular trash rather than recycling bins.
Q: Why do some thermal receipts fade over time?
A: Thermal receipts fade because the chemical coating is sensitive to environmental factors. Exposure to heat, UV light, oils (including fingerprints), and moisture breaks down the chemical reaction that created the image, causing gradual fading.
Q: How can I preserve important thermal paper receipts?
A: To preserve thermal receipts, make photocopies or digital scans immediately. Store originals in cool, dark places in acid-free paper sleeves. Avoid plastic sleeves, direct sunlight, and heat sources. Never laminate thermal receipts as heat destroys them.
Q: Are there eco-friendly thermal paper options?
A: Yes, BPA-free and phenol-free thermal papers are more eco-friendly alternatives. These papers use safer chemicals while maintaining the same functionality. Some manufacturers also offer thermal papers made from sustainably sourced materials with fewer harmful components.



























