Thermal Paper in Healthcare plays a critical role in how medical facilities operate smoothly and efficiently. From printing patient wristbands to recording ECG results, this special paper supports accuracy where it matters most—saving time and reducing errors.
In this post, you’ll learn what thermal paper is, why it’s essential in healthcare settings, and how different types like direct thermal and thermal transfer paper serve unique purposes. Whether you're managing records or improving patient safety, understanding thermal paper’s value can help streamline your healthcare operations.
Understanding Thermal Paper Technology
What is thermal paper made of?
Thermal paper is made up of three layers. The base layer is standard paper, offering structure and support. The second layer is a heat-sensitive chemical coating that reacts when heated, forming images or text. Some types include a topcoat that protects the surface from moisture, scratches, or fading, making them suitable for hospital use.

How does thermal printing work?
Thermal printing uses heat instead of ink. A thermal printer has a heated printhead that touches the coated paper. Wherever the heat is applied, the paper darkens to form the image or text. It’s fast, clean, and produces smudge-free results. Healthcare professionals often rely on it for labels, wristbands, and diagnostic reports.
Direct thermal vs. thermal transfer printing
Direct thermal printing works by applying heat directly to the specially coated paper surface to create images.It's mostly used for short-term purposes like patient check-in labels, receipts, or appointment slips.
Thermal transfer printing uses a ribbon to transfer ink onto labels, offering more durability and resistance.This method is preferred for long-lasting labels such as blood sample IDs or surgical instrument tags.
Inkless technology advantages
Thermal printers eliminate the need for ink or toner, reducing costs and simplifying maintenance for staff.
There are fewer supply interruptions, making thermal printers ideal for high-pressure medical environments.
Their simple design helps reduce mechanical problems and training requirements for busy healthcare teams.
Quick, quiet, and efficient printing supports smoother workflows in emergency rooms and laboratories.
Common Applications of Thermal Paper in Healthcare
1. Patient Identification
Thermal paper is widely used to print wristbands and ID labels for patient tracking. These wristbands include critical details like names, medical IDs, and allergies. Printed directly from a thermal printer, they’re smudge-proof and easy to scan. Hospitals use them to reduce mix-ups and help staff identify patients quickly during treatment.
Key uses:
Wristbands are used during admission for instant patient recognition.
ID labels are placed on folders, beds, or devices to match patient data.
2. Medical Records and Charts
Doctors and nurses print prescriptions, diagnostic reports, and test summaries using thermal paper. The prints are sharp and quick to produce. Because the text doesn’t smudge, it’s ideal for storing critical data safely. Most printers used for this are compact, making them perfect for busy hospital desks or mobile carts.
Used for:
3. Laboratory and Specimen Labeling
Thermal labels are essential for identifying vials, slides, or sample bags in labs. Each label usually includes a barcode, name, and timestamp. Since lab environments involve handling chemicals and refrigeration, thermal transfer labels are preferred for their durability and clarity in extreme conditions.
Why it matters:
4. Imaging and Diagnostic Reports
Thermal paper is used to print readings from ECG machines and ultrasound scans. These images help doctors interpret heart rhythms or internal structures. Thermal printers produce them instantly, with sharp contrast and reliable detail. The paper is designed to resist fading, which is key for patient monitoring and follow-up care.
Typical printouts:
5. Appointment Cards and Receipts
Front desks use thermal printers to generate appointment reminders and receipts for patient visits. These are printed within seconds and handed directly to the patient. Clear text helps reduce confusion about visit times, while printed receipts ensure transparency in billing.
Main uses:
Appointment slips that include date, time, and doctor’s name.
Billing receipts that confirm payment or insurance processing.
Types of Thermal Paper Used in Medical Settings
Direct Thermal Paper
Direct thermal paper reacts directly to heat. It doesn’t use a ribbon or ink. This makes it simple and quick for short-term printing. Hospitals often use it for printing receipts, prescription slips, or temporary labels. But it can fade if exposed to light or heat for long periods.
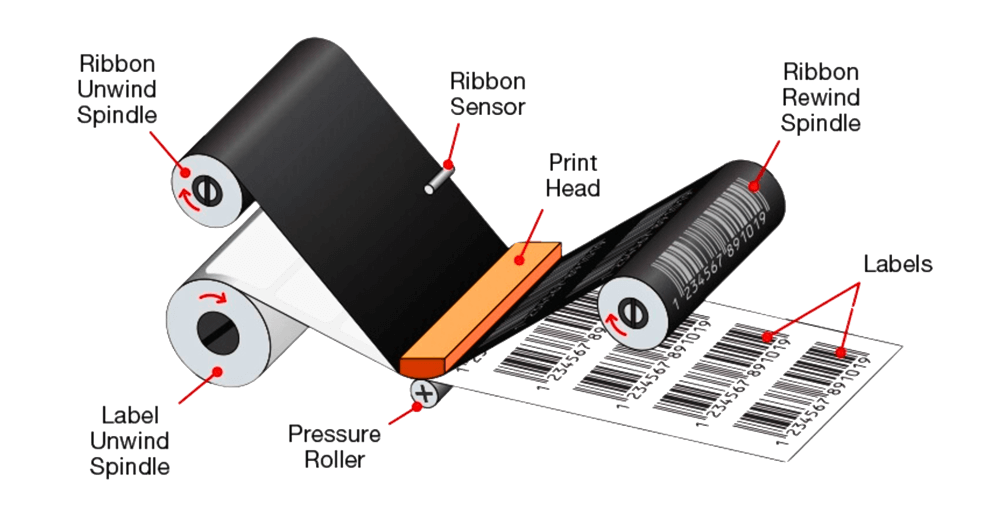
Key features:
Thermal Transfer Paper
This type uses a ribbon to transfer ink onto the paper surface. The result is more durable and long-lasting than direct thermal prints. It’s preferred in labs or pharmacies where labels must resist smudging, chemicals, or temperature changes. Common for labeling medication bottles, lab samples, and storage containers.
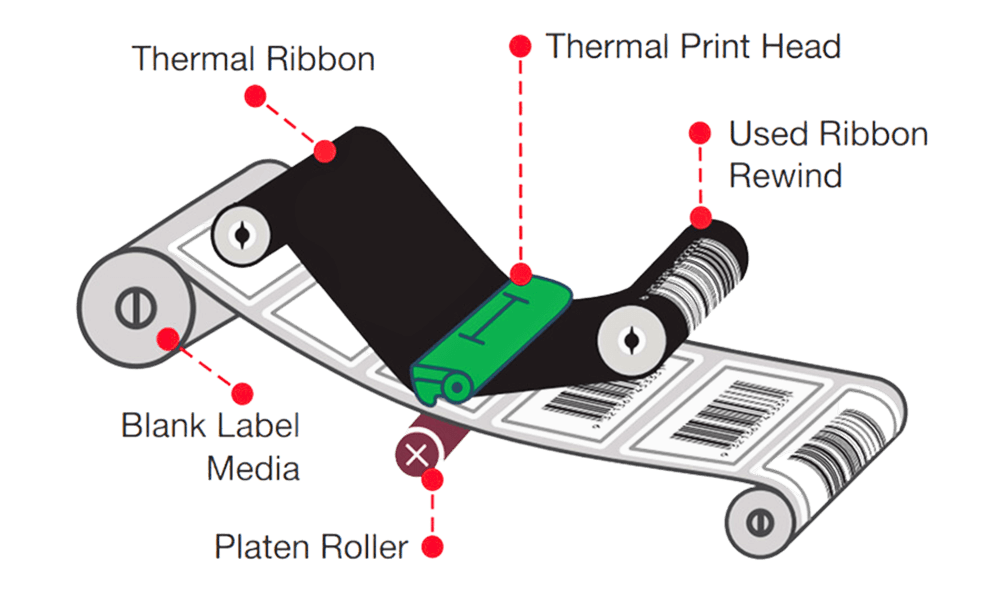
Best used when:
Labels need to survive handling, cold storage, or chemical exposure
Patient or specimen data must remain readable over weeks or months
Top-Coated Thermal Paper
Top-coated thermal paper includes an extra protective layer. It improves image sharpness and protects against scratches or moisture. It’s often used for medical records, printed charts, or wristband tags that are stored or handled frequently. The prints stay crisp, even when touched often by gloved hands.
Use cases include:
Synthetic and Self-Adhesive Thermal Paper
Synthetic thermal paper is tear-resistant and water-resistant. It’s made from plastic-based material rather than wood pulp. Hospitals use it for patient wristbands and equipment tags. Self-adhesive thermal paper includes a sticky backing, making it ideal for labeling medication or test tubes.
Ideal for:
Environments where surfaces get wet, cold, or handled frequently
Wristbands or stickers applied directly to curved or slick surfaces
Benefits of Thermal Paper in the Healthcare Industry
Speed and Efficiency in Printing
Thermal printers offer near-instant output, making them ideal for fast-paced healthcare environments. Whether printing wristbands, test labels, or patient summaries, the process is quick and reliable. Since no drying time or ink is involved, staff can immediately handle and apply printed materials, helping reduce delays during emergencies or routine check-ins.
High Legibility and Accuracy
Thermal paper produces dark, high-contrast text that’s easy to read and scan. This matters most when dealing with barcodes, medication instructions, and test labels. Clear, consistent prints help reduce misidentification and reading errors. In labs and wards, this accuracy plays a key role in patient safety and seamless communication between departments.
Cost-Effectiveness for Healthcare Facilities
No ink or toner is needed in direct thermal printers, reducing supply expenses.
Fewer mechanical parts result in lower repair and maintenance costs over time.
On-demand printing prevents wasted sheets, especially when only one label is needed.
Hospitals can cut printing-related downtime, keeping operations smooth and cost-efficient.
Easy Integration with EMR and EHR Systems
Thermal printers are often compatible with digital health systems. They can auto-generate patient labels or ID wristbands as soon as data is entered into EMR/EHR software. This ensures printed information matches digital records without manual copying. The result is better workflow, fewer entry errors, and improved tracking across patient care.
| Integrated Print Task | Common Use Location | Benefit |
| Patient ID wristbands | Admissions, ER | Fast check-in and clear identification |
| Lab sample labels | Pathology, testing labs | Barcode tracking for accurate results |
| Prescription slips | Pharmacy, mobile units | Quick medication labeling and handover |
Portability for Mobile Healthcare Units
Compact thermal printers are easy to transport, making them perfect for mobile clinics, ambulances, or in-home visits. Staff can print patient IDs, receipts, or care summaries on the spot. Without bulky devices or complicated setups, mobile teams gain speed and flexibility, especially when responding to patients in remote or crowded areas.
Choosing the Right Thermal Paper for Healthcare Needs
Factors to Consider
When selecting thermal paper, it's important to think about how and where it will be used. Hospitals, labs, and clinics all have different demands. Choosing the wrong paper may lead to fading prints, label detachment, or unreadable barcodes—so matching features to the task is key.
Durability
Choose more durable thermal paper for labels exposed to frequent handling, chemicals, or cleaning fluids.
Long-term items like specimen tags or patient charts need paper that resists wear and image fading over time.
Top-coated and synthetic papers are often better suited for critical applications in busy clinical environments.
Sensitivity to Heat and Moisture
Direct thermal paper can fade if exposed to strong heat or direct sunlight, making it unreliable for long-term storage.
In humid environments, poorly coated paper may smudge or darken unintentionally, leading to unreadable data.
Moisture-resistant options are recommended in labs, near sinks, or in surgical preparation areas.
Label Adhesives and Surface Types
Not all thermal labels stick equally well to every surface—vials, tubes, and plastic trays may need stronger adhesives.
For curved or damp surfaces, flexible and high-tack labels prevent peeling and misplacement.
Self-adhesive thermal papers with synthetic backings offer better performance on metal or plastic medical tools.
Matching Paper Types with Medical Applications
Each type of thermal paper works best in specific medical settings. Using the wrong type can affect readability, patient safety, or compliance. Here's a quick breakdown:
| Medical Application | Recommended Paper Type | Reason |
| Short-term prescriptions | Direct Thermal Paper | Fast, low-cost, suitable for daily use |
| Patient wristbands | Synthetic Self-Adhesive Paper | Durable, waterproof, tear-resistant |
| Lab samples and blood vials | Thermal Transfer Paper | Long-lasting, chemical-resistant |
| Archival medical records | Top-Coated Thermal Paper | High clarity, resistant to fading |
| Field or mobile print jobs | Direct Thermal or Synthetic | Compact, simple, moisture-resistant |
Common Thermal Printer Machines in Healthcare
Popular Models
In healthcare, thermal printers like Zebra, Star Micronics, and GE Healthcare devices are widely used. These brands offer reliable and efficient solutions for printing patient labels, prescriptions, and medical records. Zebra's QLN Series, for example, provides mobile printing flexibility, while Star Micronics' TSP100 series offers compact, fast printing.
Features That Matter in Medical Environments
When choosing a thermal printer for healthcare, compatibility, speed, and durability are key. Printers must work seamlessly with hospital software and handle high volumes of prints. Speed is crucial in emergency situations, while durability ensures long-term reliability, especially in challenging hospital environments.
Direct Thermal vs. Thermal Transfer Printer Selection Tips
Direct Thermal Printers: Ideal for short-term use; prints fade over time but are cost-effective.
Thermal Transfer Printers: More durable, perfect for long-lasting labels but require a ribbon. Choosing between them depends on your specific needs, like label lifespan and budget.
Thermal Paper for Medical Imaging

ECG Thermal Paper
ECG thermal paper plays a critical role in capturing precise heart rhythms. The clarity of the printout is essential, as any blur could lead to misinterpretation. High-quality thermal paper ensures that each detail of the ECG waveform is clear and sharp for accurate diagnosis.
Ultrasound Thermal Paper
In ultrasound imaging, thermal paper is used to print high-contrast images of organs and tissues. The sharpness and contrast of the printout are crucial for accurate diagnostics. Ultrasound paper ensures that every detail of the image is preserved, aiding healthcare professionals in making quick, accurate decisions.
Fetal Monitoring and OB/GYN Applications
Thermal paper is widely used in fetal monitoring and OB/GYN applications to record vital signs like fetal heart rates. The paper’s durability is key, as these records must be kept for future reference. Clear prints are essential in monitoring patient health and ensuring that no details are missed during examinations.
Challenges and Considerations
Thermal Image Fading and Storage Limitations
One challenge with thermal paper is its tendency to fade over time. In healthcare, this can affect the legibility of medical records. Proper storage in cool, dark places is necessary to preserve the clarity of the images.
Handling and Storage Best Practices in Hospitals
In hospitals, thermal paper should be stored away from heat and light. It’s best kept in a dry, dark area to prevent fading. Handling it carefully, without excessive touching, also ensures the images remain clear and readable.
Compliance with Healthcare Record-Keeping Regulations
Healthcare facilities must ensure their thermal paper records comply with medical record-keeping regulations. This includes ensuring that printed materials meet quality standards for long-term storage and are easily accessible when needed for audits or reviews.
Future Trends in Thermal Printing for Healthcare
Innovations in Thermal Paper Technology
New thermal paper coatings will enhance image durability, reducing fading over time.
Future developments may include eco-friendly materials that maintain high quality while being more sustainable.
Integration with Digital Systems and Automation
Thermal printers will increasingly integrate with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems for seamless printing.
Automation in hospitals will streamline documentation, improving efficiency in patient care.
Role in Telemedicine and Portable Health Units
Portable thermal printers are expected to grow in telemedicine, enabling remote diagnostics and patient monitoring.
They’ll allow healthcare providers to print essential patient information on-site, improving communication in remote settings.
Conclusion
Thermal paper plays a critical role in the healthcare industry, offering benefits like speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. It is essential for patient identification, medical records, and diagnostic imaging. Despite the rise of digital systems, thermal paper remains vital due to its reliability, ease of use, and compatibility with medical equipment.
As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, thermal paper's enduring role in ensuring fast, clear documentation and patient safety cannot be overlooked. Embrace the future of thermal printing for improved healthcare outcomes and efficiency.
FAQs
What is the difference between direct thermal and thermal transfer paper?
Direct thermal paper uses heat to create images, while thermal transfer uses a ribbon for a more durable print.
How long does thermal paper last in medical records?
Thermal paper can last between 1 to 7 years, depending on storage conditions and paper quality.
Is thermal paper safe for patient use?
Yes, thermal paper is safe for patient use, as it’s non-toxic and widely used in medical environments.
Can thermal paper be used in high-temperature hospital environments?
Thermal paper can be sensitive to heat, so it should be stored away from high temperatures to maintain image quality.
Reference Sources
[1] https://telemarkcorp.com/industries/healthcare-industry-solutions/
[2] https://pandapaperroll.com/thermal-paper-in-healthcare/
[3] https://cyrixhealthcare.com/Understanding-the-Significance-of%20Thermal-Paper-in-Medical-Recording-updated-content.php
[4] https://blog.caresfield.com/thermal-printers-in-healthcare-an-overview-of-best-uses-considerations-and-maintenance





























