
Have you ever tried using regular paper in a thermal printer and ended up with a blank sheet? That’s because thermal printers don’t work like inkjet or laser printers. Instead of ink, they rely on heat-sensitive paper to produce clear, lasting prints.
Using the right paper is crucial for efficiency and print quality. Without special thermal paper, these printers simply can’t function. Whether for receipts, shipping labels, or medical tags, the correct paper ensures durability and accuracy.
In this post, we’ll explain why thermal printers need special paper, how different types work, and what happens if you use the wrong one.
What is Thermal Paper?
Thermal paper is a special type of paper that is coated with a heat-sensitive material. This material changes color when exposed to heat, allowing images and text to be printed without the need for ink or toner.
Key characteristics of thermal paper include:
Heat-sensitive coating: Thermal paper has a special coating that reacts to heat. When the coating is exposed to the high temperatures of a thermal print head, it changes color to create the desired print.
Inkless printing: Because the printing process relies on heat rather than ink, thermal paper allows for printing without the need for costly and messy ink or toner cartridges.
Thermal paper typically consists of several layers:
Base layer: This layer provides structure and support for the thermal paper. It is usually made of regular paper or a plastic film.
Thermal coating layer: This is the layer that contains the heat-sensitive chemicals. When exposed to heat from the thermal print head, this coating activates and changes color to form the printed image or text.
Protective layer (optional): Some thermal papers include an additional protective layer on top of the thermal coating. This layer helps prevent the printed image or text from fading when exposed to light, heat, or chemicals.
These layers work together to enable the thermal printing process. When heat is applied to specific areas of the thermal paper by the thermal print head, the coating reacts to create the desired text or image. Thermal paper is known for its ease of use and fast printing speeds, making it widely used across various applications.
How Thermal Printing Works
Thermal printing is a direct printing process that uses heat to produce images and text on special thermal paper. This printing method offers several advantages over traditional ink-based printing. Let's take a closer look at how it works.
Direct Thermal Printing Process
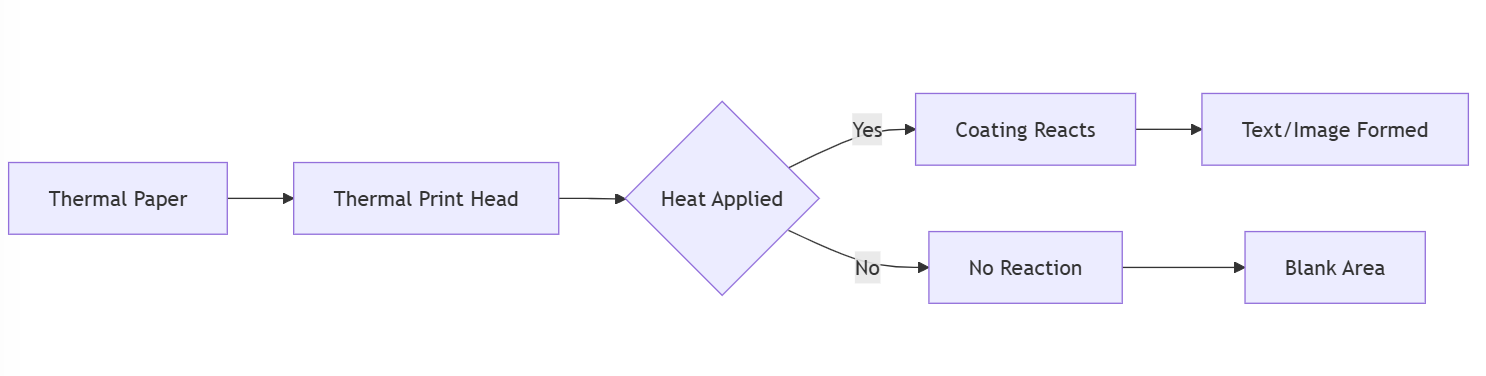
Print head applies heat: The thermal print head contains numerous small heating elements. As the thermal paper passes over the print head, these elements selectively apply heat to specific areas of the paper.
Coating reacts to heat: The heat-sensitive coating on the thermal paper reacts to the applied heat. In the areas where heat is applied, the coating undergoes a chemical reaction and changes color, typically to black. This color change creates the desired text or images on the paper.
The direct thermal printing process is illustrated in the diagram below:
Advantages of Thermal Printing
Thermal printing offers several benefits compared to traditional ink-based printing methods:
Fast and efficient: Thermal printers can produce high-speed prints, making them ideal for applications requiring quick output, such as receipts and labels.
High-quality prints: The direct thermal printing process creates sharp, clear images and text. The prints are resistant to smudging and fading, ensuring long-lasting readability.
No ink or toner required: Thermal printers do not rely on ink or toner cartridges. This eliminates the need for frequent replacements, reducing overall printing costs and maintenance requirements.
| Advantages | Description |
| Speed | Fast printing for quick output |
| Quality | Sharp, clear, and long-lasting prints |
| Cost-effective | No ink or toner cartridges needed |
Differences Between Thermal Paper and Regular Paper
Thermal paper and regular paper serve different purposes. Their composition, cost, and usage vary, making each suitable for specific printing methods.
Material and Coating
Thermal paper has a heat-sensitive coating that reacts to heat, producing clear images without ink. This coating consists of chemical compounds that change color when exposed to the thermal print head.
Regular paper lacks this coating. It requires ink, toner, or ribbons to generate text or images.
Thickness
Thermal paper is slightly thinner than standard printer paper. Its smooth surface ensures quick, precise printing. Regular paper varies in thickness, depending on its type (copy paper, cardstock, or glossy paper).
| Feature | Thermal Paper | Regular Paper |
| Coating | Heat-sensitive chemical layer | No special coating |
| Printing Method | Uses heat to create images | Requires ink or toner |
| Thickness | Thinner, smooth surface | Varies based on type |
Cost
Thermal paper costs more due to its special chemical coating. The manufacturing process involves multiple layers, ensuring durability and heat sensitivity. Regular paper is more affordable, widely available, and used for general printing.
Intended Use
Thermal paper works exclusively in thermal printers. It is commonly used for receipts, labels, and tickets. Regular paper is compatible with inkjet and laser printers, making it ideal for documents, reports, and photos.
Can You Use Regular Paper in a Thermal Printer?
One common question that arises when using thermal printers is whether they can accommodate regular paper. While it may be tempting to use standard paper in a thermal printer, it is not recommended. Using regular paper can lead to several issues and may even damage the printer.
Problems with Using Regular Paper
Poor print quality: Thermal printers are designed to work with thermal paper, which has a special heat-sensitive coating. When regular paper is used, the print head cannot generate the necessary heat reaction, resulting in blurry, unclear, or even unreadable text and images.
Potential damage to print head: Thermal printers attempt to heat the coating that is not present on regular paper. This can cause the print head to overheat or sustain damage. Since the print head is a critical component of a thermal printer, overheating or damage can negatively impact the printer's overall performance and may require repair or replacement.
Paper feed issues: Thermal printers are typically designed to accommodate specific paper feeding mechanisms for thermal paper. The thickness, size, and feeding mechanisms of regular paper may not match those of thermal paper, leading to paper jams or uneven paper feeding, which can affect print quality and the printer's normal functioning.
Additional Supply Costs
Using regular paper in a thermal printer may require alternative printing supplies.
| Factor | Thermal Paper | Regular Paper |
| Ink/Toner Needed | No | Yes |
| Maintenance Cost | Low | High |
| Print Speed | Fast | Slower |
Using ink or toner negates thermal printing’s cost-saving benefits. Businesses choosing thermal printing often do so for efficiency and lower operational costs.
Importance of Using Manufacturer-Recommended Thermal Paper
To ensure optimal print quality and device longevity, it is crucial to use thermal paper specifically recommended by the printer manufacturer when purchasing and using a thermal printer. Manufacturers design their printers to work seamlessly with specific thermal paper types, taking into account factors such as thickness, coating quality, and thermal sensitivity.
| Consequences of Using Regular Paper | Importance of Manufacturer-Recommended Paper |
- Poor print quality
- Potential print head damage
- Paper feed issues
- Increased supply costs | - Ensures optimal print quality
- Protects printer from damage
- Prevents paper feed problems
- Maintains cost-effectiveness |

Choosing the Right Thermal Paper for Your Printer
Selecting the appropriate thermal paper for your printer is crucial to ensure optimal performance and print quality. Several factors must be considered when choosing thermal paper, including compatibility, durability, and environmental exposure. Additionally, understanding common sizes, formats, and quality standards can help you make an informed decision.
Factors to Consider
Printer Type Compatibility: Different thermal printers may require specific types of thermal paper. Always check your printer manufacturer's recommendations to ensure the paper you choose is compatible with your device. Using incompatible paper can lead to poor print quality or even damage to the printer.
Durability Requirements: Consider the intended use and lifespan of your printed materials. If you need prints to last for an extended period, look for thermal paper with higher durability ratings. For short-term use, such as receipts, a standard thermal paper grade may suffice.
Environmental Exposure: Take into account the environmental conditions your prints will be exposed to. If your prints will be subjected to high temperatures, direct sunlight, or moisture, choose thermal paper designed to withstand these conditions. Look for options with protective coatings or special treatments to enhance durability.
Common Sizes and Formats
Rolls vs. Sheets: Thermal paper is available in both roll and sheet formats. Rolls are the most common choice for receipt printers and label makers, while sheets are often used for specialized applications. Consider your printer's specifications and the intended use to determine the most suitable format.
Standard Receipt Paper Sizes: Common receipt paper roll sizes include:
These sizes are widely used in point-of-sale systems, credit card terminals, and cash registers.
2 1/4" (57mm) x 85'
3 1/8" (80mm) x 230'
3 7/16" (87mm) x 200'
4 3/8" (111mm) x 85'
Industrial Label Sizes: For industrial labeling applications, popular sizes include:
Choose a size that accommodates your label content and fits your printer's specifications.
4" x 6"
4" x 2"
2" x 1"
4" x 1"
Certifications and Quality Standards
BPA-Free and Eco-Friendly Options: Some thermal papers may contain Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that can have harmful effects on human health and the environment. If sustainability and safety are a concern, opt for BPA-free thermal paper. Look for options made from recycled materials or those that are certified as eco-friendly.
Recognized Thermal Paper Manufacturers: Stick with reputable thermal paper manufacturers, they are known for producing high-quality, consistent products. Some recognized brands in the industry include:
Sunrise
Appvion
Koehler Paper
Mitsubishi HiTec Paper
Oji Paper
Ricoh
By choosing thermal paper from trusted manufacturers, you can ensure reliability and compatibility with your printer.
| Factor | Consideration |
| Printer Compatibility | Ensure paper is compatible with your specific printer model |
| Durability | Choose paper with appropriate durability for your application |
| Environmental Exposure | Select paper that can withstand the expected environmental conditions |
| Size and Format | Match the paper size and format to your printer and intended use |
| Certifications | Opt for BPA-free and eco-friendly options when possible |
| Manufacturer | Stick with recognized thermal paper manufacturers for quality and reliability |

Common Applications of Thermal Paper
Thermal paper is widely used in commercial and personal settings. Its fast, ink-free printing makes it ideal for receipts, labels, and documents that require quick processing.
Commercial Uses
Receipts and tickets: Thermal paper is commonly used in retail stores, supermarkets, restaurants, and gas stations for printing receipts and tickets. It enables quick and clear printing of transaction details.
Banking and finance: Banks, ATMs, and self-service kiosks utilize thermal printing technology for generating transaction receipts, account statements, and deposit confirmations.
Healthcare: Hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies employ thermal printers for printing prescriptions, medical reports, patient labels, and medication labels.
Logistics and transportation: The logistics and transportation industry uses thermal paper for printing shipping labels, transportation documents, courier receipts, and package labels.
Hospitality and tourism: Hotels, car rental companies, and airlines adopt thermal printing for creating room receipts, itineraries, boarding passes, and baggage tags.
Entertainment and events: Movie theaters, concert venues, and sports stadiums use thermal printers for printing tickets, entry passes, and food and beverage orders.
Personal Uses
Planners and journals: Thermal paper is perfect for creating custom stickers and decorations for planners and journals.
To-do lists: Users can easily print to-do lists and reminders for personal organization.
Photo printing: Small photos can be printed for scrapbooking, photo albums, and decorative purposes.
Home organization: Custom labels can be designed and printed for organizing items within the home, such as kitchen containers and storage boxes.
The table below summarizes the common applications of thermal paper:
| Commercial Uses | Personal Uses |
- Receipts and tickets
- Banking and finance
- Healthcare
- Logistics and transportation
- Hospitality and tourism
- Entertainment and events | - Planners and journals
- To-do lists
- Photo printing
- Home organization |

Conclusion
Thermal printers require special heat-sensitive paper to function. Regular paper won’t react to heat, leading to blank or damaged prints.
Thermal paper has a chemical coating that responds to heat, producing clear, high-quality images. Without it, printing fails.
Choose paper that matches your printer type. Look for BPA-free, fade-resistant, and high-durability options for long-term use.
Interested in thermal paper? Sunrise Industry provides reliable, high-quality options for various applications. Their products meet industry standards and support eco-friendly solutions. Contact Sunrise today for details on sizes, coatings, and bulk orders. Get the right thermal paper for your business needs.
FAQs About Thermal Paper and Printers
Is thermal paper toxic?
Some thermal papers may contain Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that has been linked to potential health risks. However, many manufacturers now offer BPA-free thermal paper options. If you are concerned about toxicity, look for thermal paper specifically labeled as BPA-free.
Can I use thermal paper in a regular printer?
No, you should not use thermal paper in a regular printer. Thermal paper is designed to work specifically with thermal printers. It has a special heat-sensitive coating that reacts to the heat from the thermal print head. Using thermal paper in a regular printer may cause damage to the printer and will not produce the desired print results.
How long does thermal paper last?
The lifespan of thermal paper varies depending on several factors, such as the quality of the paper, storage conditions, and exposure to heat and light. On average, thermal paper prints can last for several years under proper storage conditions. However, if you need your prints to last for an extended period, consider using thermal paper with higher durability ratings or opt for thermal transfer printing instead.
Are there eco-friendly thermal paper options?
Yes, there are eco-friendly thermal paper options available. Some manufacturers offer thermal paper made from recycled materials or paper sourced from sustainably managed forests. Additionally, you can look for thermal paper that is BPA-free and phenol-free, as these chemicals can have negative environmental impacts.
What causes thermal paper to turn black?
Thermal paper turns black when it is exposed to heat. The heat-sensitive coating on the paper reacts to high temperatures, causing it to darken. This can happen if the paper is exposed to direct sunlight, heat sources, or friction. To prevent thermal paper from turning black prematurely, store it in a cool, dry place away from heat and light.
How should I store unused thermal paper rolls?
To ensure the longevity and quality of your unused thermal paper rolls, follow these storage tips:
Store thermal paper in a cool, dry place with a stable temperature, ideally between 64°F and 77°F (18°C and 25°C).
Keep the paper away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and high humidity.
Store the rolls in their original packaging or a sealed container to protect them from dust and moisture.
Avoid storing thermal paper near chemicals or solvents, as they can react with the heat-sensitive coating.
Use older rolls first to minimize the risk of deterioration over time.



























